オールペン作業です!
2022年03月02日
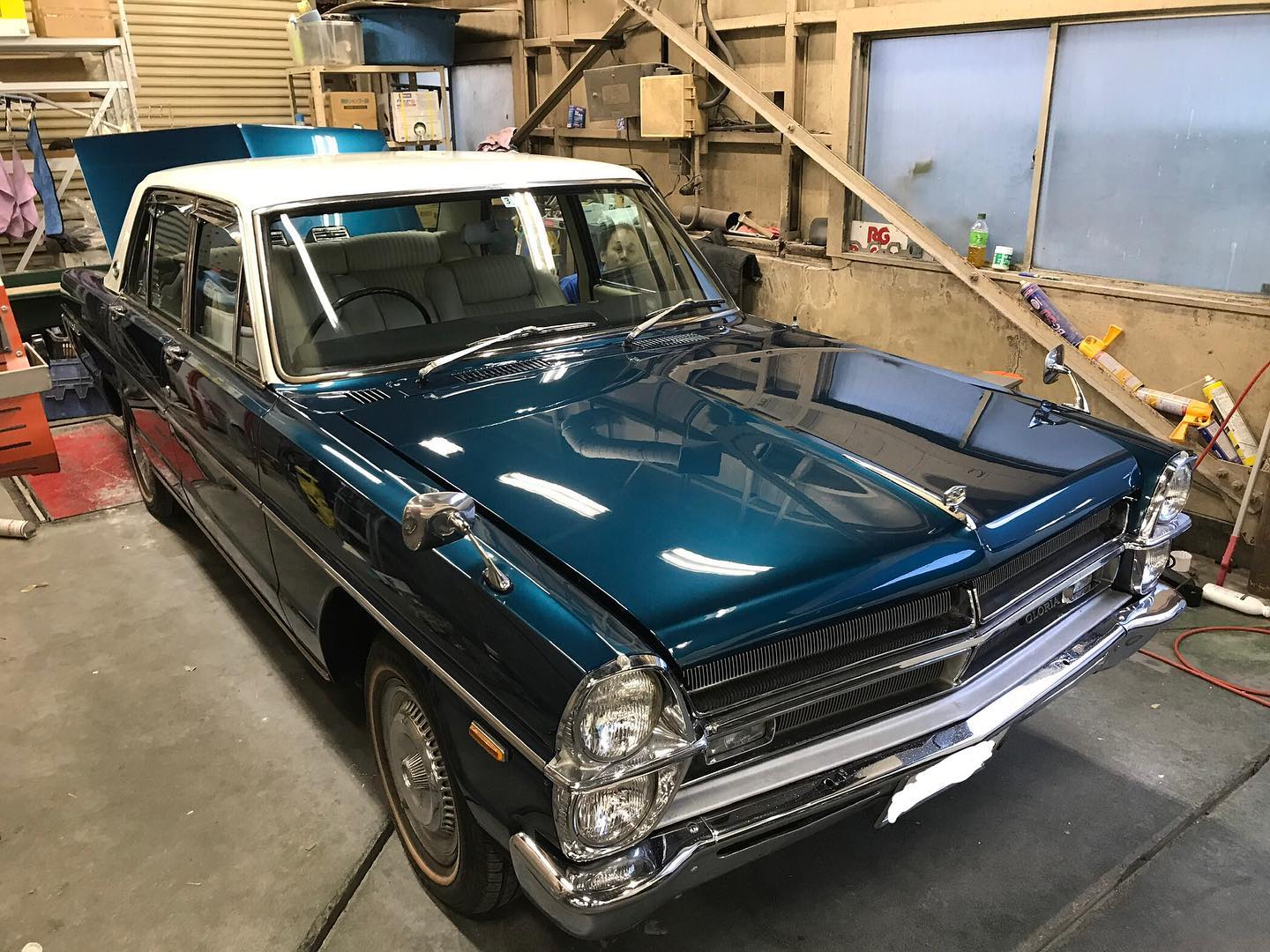
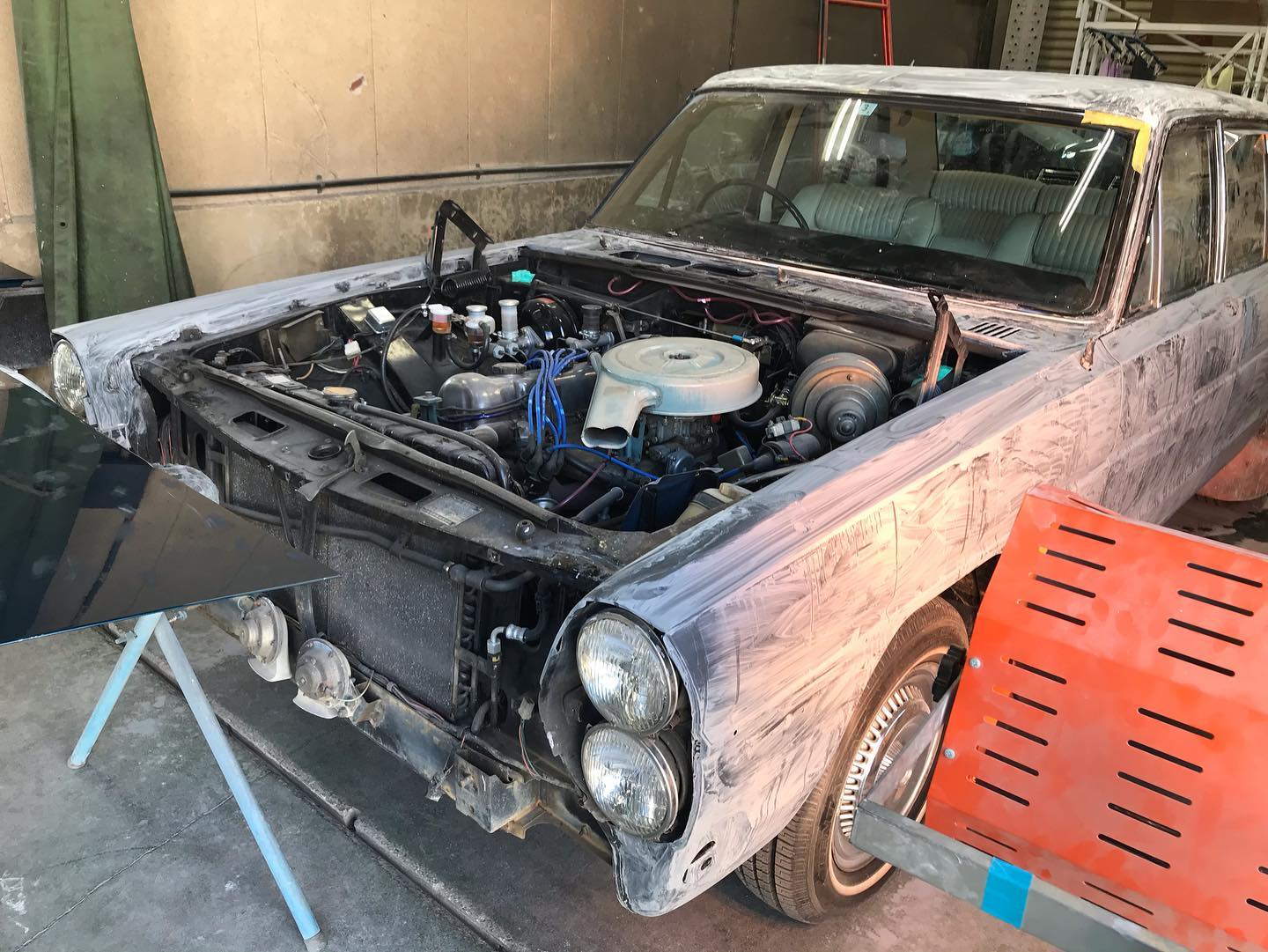
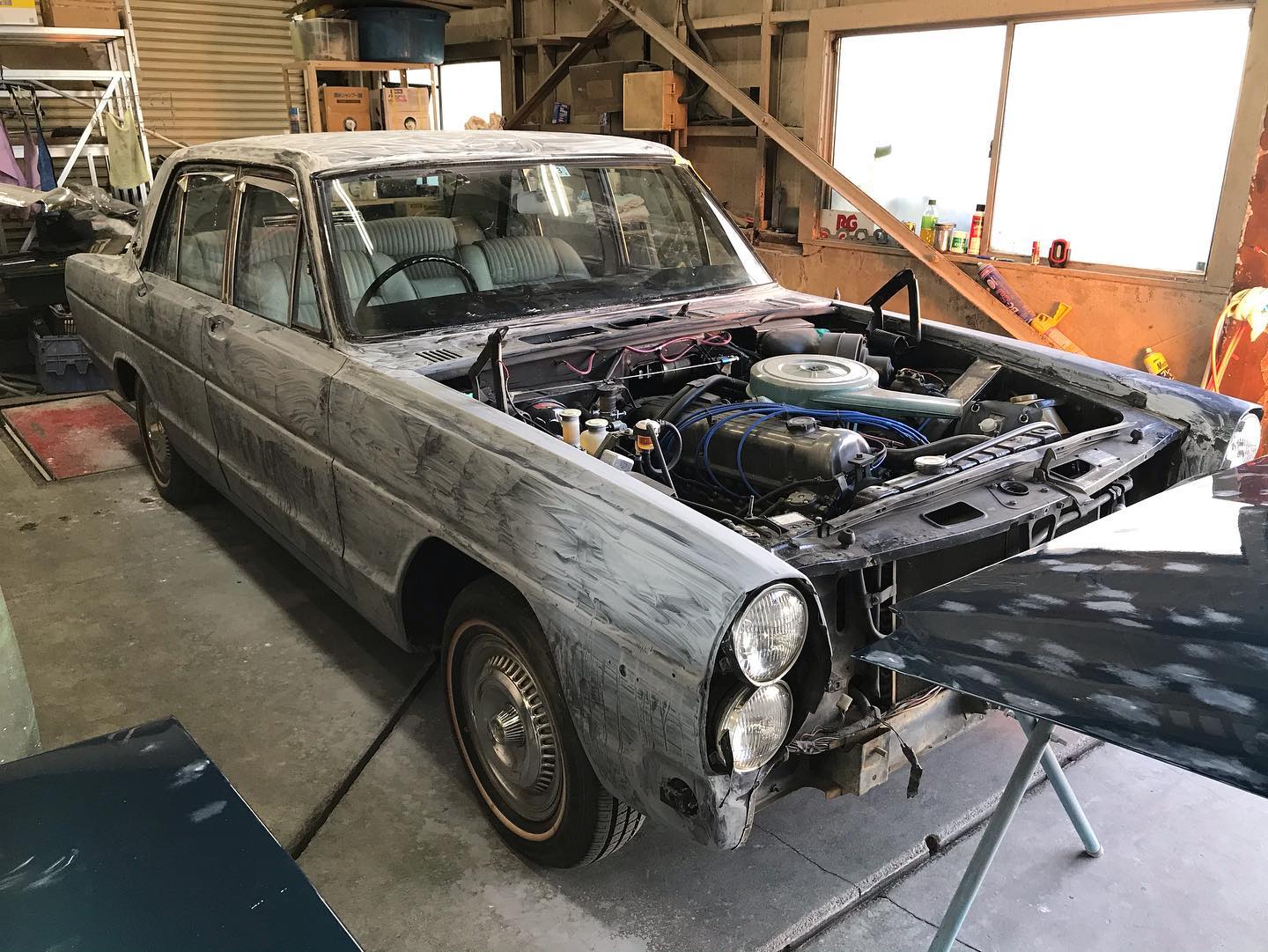
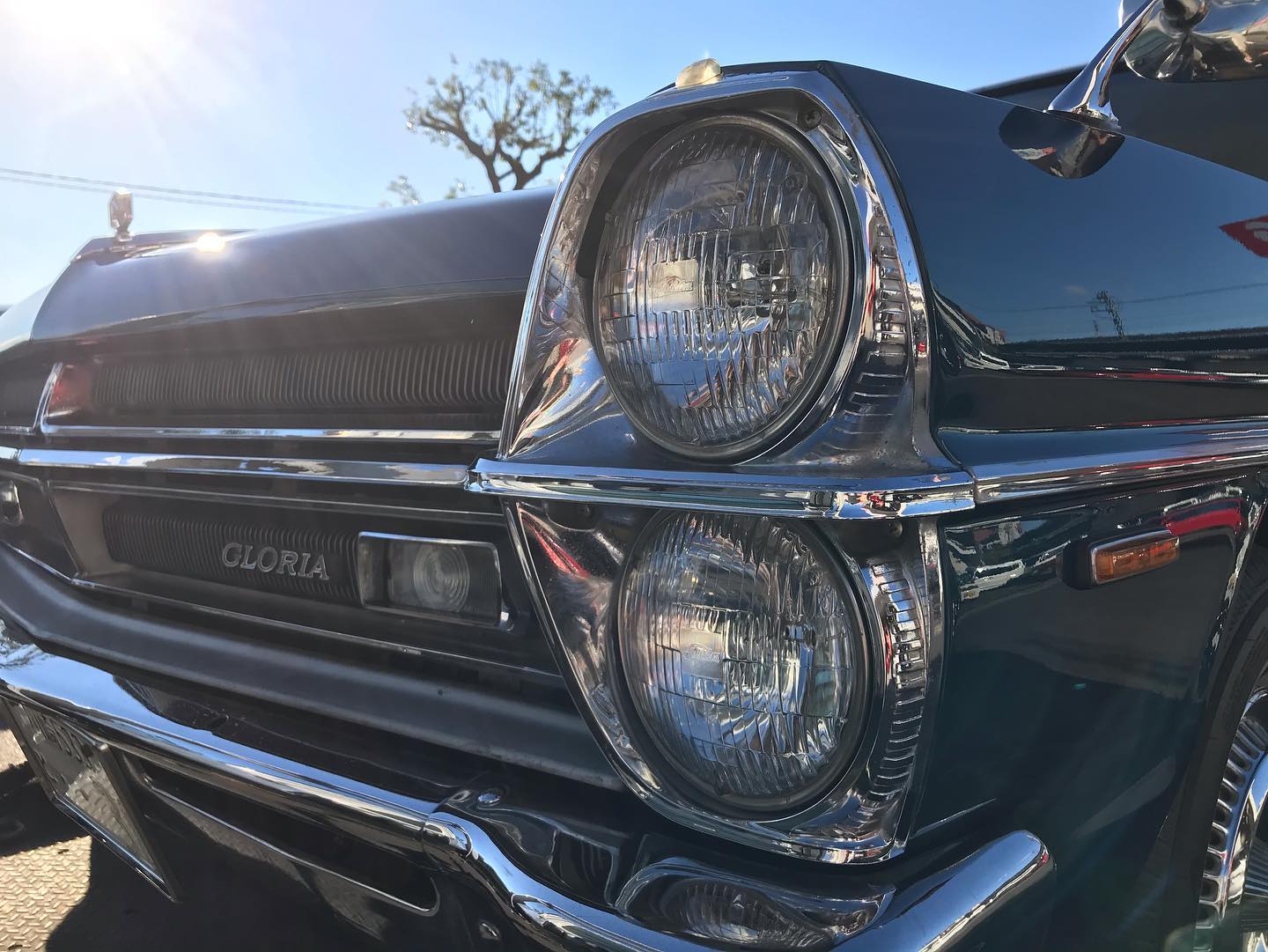
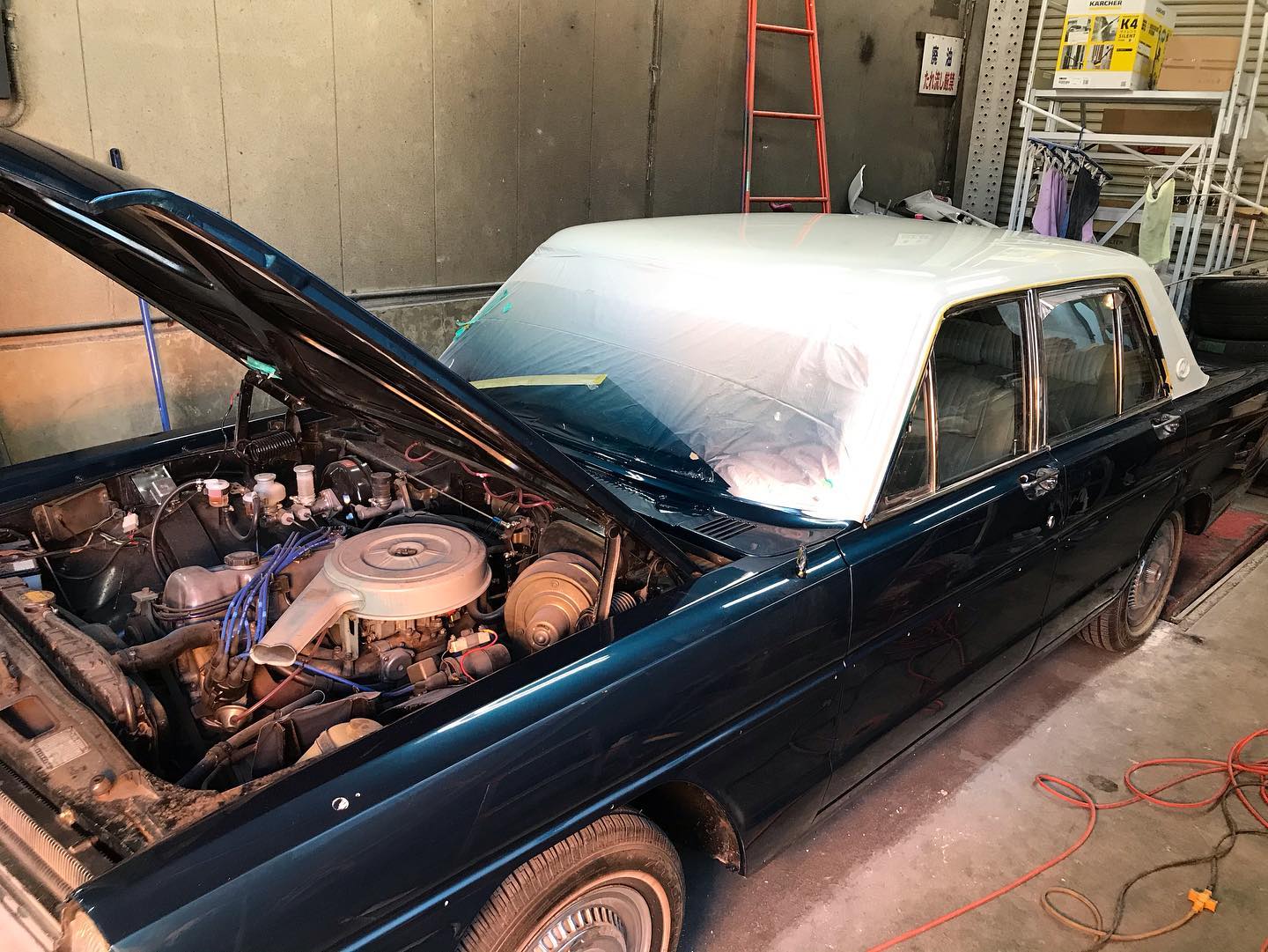
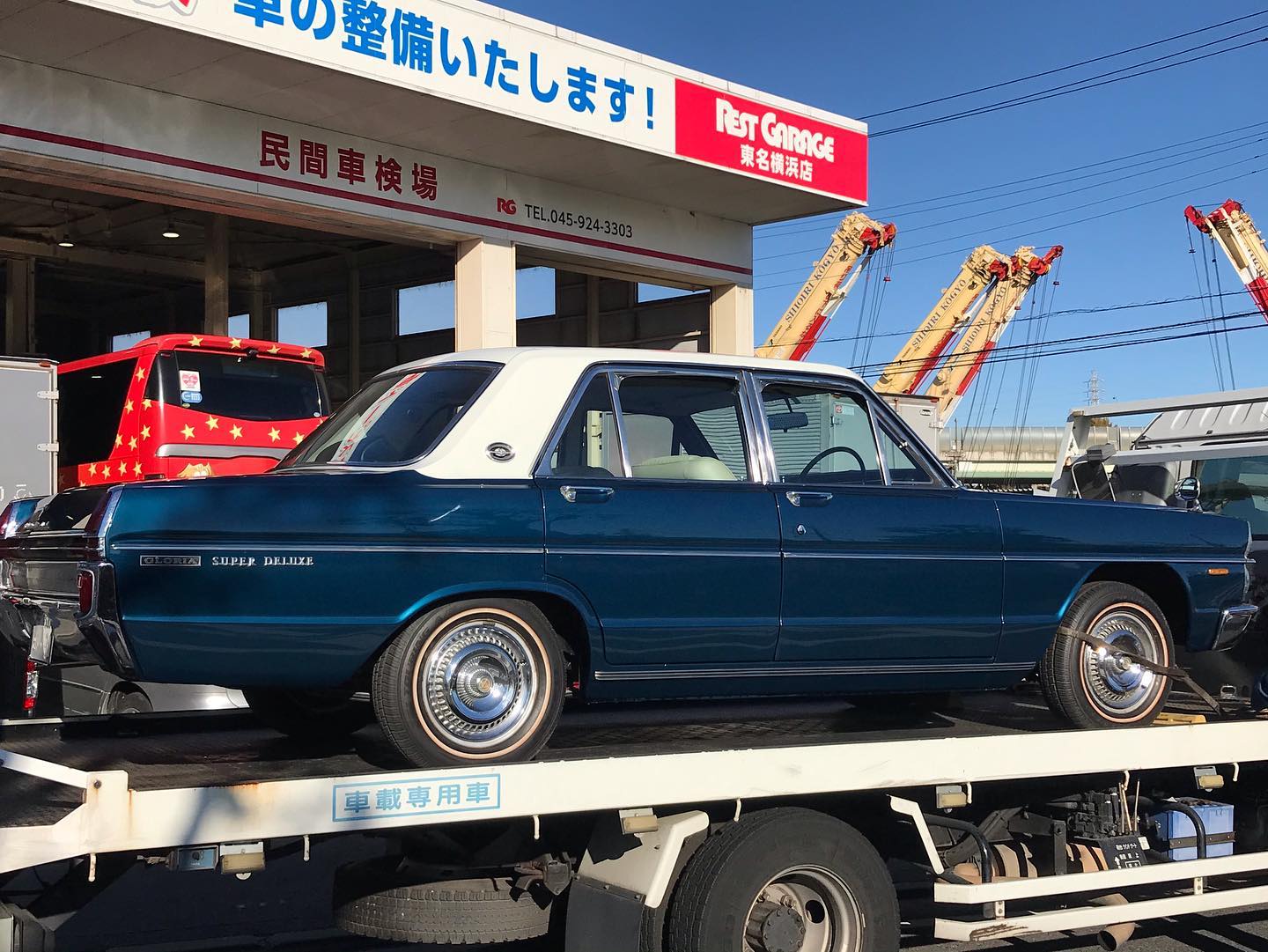






熟練の職人が丁寧に仕上げました。
オールドカーの整備、板金も弊社にお任せください。
ご満足して頂けると思います。
この記事へのコメント
(Dena)
BPC?157 is a synthetic peptide that mimics a naturally occurring segment
of body protection compound 157, which is derived from a protein found in the stomach lining.
The sequence consists of 15 amino acids and has attracted significant interest for its potential regenerative properties
across various tissues, including skin, muscle, tendon, nerve,
and even bone. Researchers have explored BPC?157 mainly through animal models, noting rapid improvements in wound closure rates, reduced inflammation, and enhanced angiogenesis?the formation of new blood vessels that supply nutrients to healing sites.
In the context of a health library?a curated repository of
medical literature, clinical trial data, and peer?reviewed studies?BPC?157 occupies
a niche as an investigational agent. Most entries in such libraries highlight its experimental status, noting that
while preclinical results are promising, human trials remain limited.
The literature emphasizes safety profiles observed in rodents and
rabbits, with no serious adverse events reported at doses used for wound healing or
tendon repair.
One of the most compelling benefits documented is how BPC?157 speeds up the wound
healing process. When applied orally, the peptide appears to circulate systemically and reach
injury sites, where it promotes cellular proliferation and collagen deposition. Studies
on skin lacerations in rats have shown that oral administration leads to a 50?70%
reduction in healing time compared with untreated controls.
In muscle injuries, BPC?157 has been observed to
accelerate myofiber regeneration, decreasing scar
tissue formation and restoring functional strength more
quickly.
Beyond superficial wounds, the peptide’s effects on deeper tissues are
noteworthy. For tendon tears?common among athletes?the oral form of BPC?157 has been reported to enhance fibroblast activity, increasing tenocyte proliferation and aligning collagen fibers in a manner that restores tensile integrity faster than conventional therapies.
In nerve injury models, such as sciatic nerve transections, researchers noted that systemic delivery of the peptide facilitated remyelination and improved motor function recovery
within weeks.
The mechanism underlying these rapid healing responses appears to involve
modulation of key signaling pathways. BPC?157 interacts with
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor beta (TGF?β), both crucial
for angiogenesis and fibrosis regulation. Additionally, it may upregulate nitric oxide synthase, thereby
improving blood flow to damaged areas and delivering oxygen and nutrients
essential for tissue repair.
Clinical anecdotal reports from users of oral BPC?157 capsules describe noticeable reductions in pain and swelling after injuries, with many citing a faster return to normal activity levels.
While these testimonies are not substitutes for controlled trials, they align with laboratory findings that the peptide can mitigate inflammatory cascades and promote regenerative
pathways.
In summary, BPC?157 represents an intriguing therapeutic candidate whose oral administration has been linked
to accelerated wound healing across multiple tissue types.
Health libraries continue to compile evidence from animal studies, noting its safety
profile and potent regenerative effects, while awaiting robust human data to confirm
efficacy and optimal dosing protocols for clinical use.
of body protection compound 157, which is derived from a protein found in the stomach lining.
The sequence consists of 15 amino acids and has attracted significant interest for its potential regenerative properties
across various tissues, including skin, muscle, tendon, nerve,
and even bone. Researchers have explored BPC?157 mainly through animal models, noting rapid improvements in wound closure rates, reduced inflammation, and enhanced angiogenesis?the formation of new blood vessels that supply nutrients to healing sites.
In the context of a health library?a curated repository of
medical literature, clinical trial data, and peer?reviewed studies?BPC?157 occupies
a niche as an investigational agent. Most entries in such libraries highlight its experimental status, noting that
while preclinical results are promising, human trials remain limited.
The literature emphasizes safety profiles observed in rodents and
rabbits, with no serious adverse events reported at doses used for wound healing or
tendon repair.
One of the most compelling benefits documented is how BPC?157 speeds up the wound
healing process. When applied orally, the peptide appears to circulate systemically and reach
injury sites, where it promotes cellular proliferation and collagen deposition. Studies
on skin lacerations in rats have shown that oral administration leads to a 50?70%
reduction in healing time compared with untreated controls.
In muscle injuries, BPC?157 has been observed to
accelerate myofiber regeneration, decreasing scar
tissue formation and restoring functional strength more
quickly.
Beyond superficial wounds, the peptide’s effects on deeper tissues are
noteworthy. For tendon tears?common among athletes?the oral form of BPC?157 has been reported to enhance fibroblast activity, increasing tenocyte proliferation and aligning collagen fibers in a manner that restores tensile integrity faster than conventional therapies.
In nerve injury models, such as sciatic nerve transections, researchers noted that systemic delivery of the peptide facilitated remyelination and improved motor function recovery
within weeks.
The mechanism underlying these rapid healing responses appears to involve
modulation of key signaling pathways. BPC?157 interacts with
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transforming growth factor beta (TGF?β), both crucial
for angiogenesis and fibrosis regulation. Additionally, it may upregulate nitric oxide synthase, thereby
improving blood flow to damaged areas and delivering oxygen and nutrients
essential for tissue repair.
Clinical anecdotal reports from users of oral BPC?157 capsules describe noticeable reductions in pain and swelling after injuries, with many citing a faster return to normal activity levels.
While these testimonies are not substitutes for controlled trials, they align with laboratory findings that the peptide can mitigate inflammatory cascades and promote regenerative
pathways.
In summary, BPC?157 represents an intriguing therapeutic candidate whose oral administration has been linked
to accelerated wound healing across multiple tissue types.
Health libraries continue to compile evidence from animal studies, noting its safety
profile and potent regenerative effects, while awaiting robust human data to confirm
efficacy and optimal dosing protocols for clinical use.
[2025-10-06 20:07:50.052558]
URL
(Chasity)
CJC?1295 and Ipamorelin are two peptides
that have gained popularity in the field of growth hormone therapy due to their ability to stimulate natural production of human growth
hormone (GH) while offering distinct pharmacokinetic profiles.
The combination is often referred to as a "growth hormone secretagogue" duo,
with CJC?1295 acting primarily as a sustained release analogue and Ipamorelin serving as a potent, selective GH?releasing peptide (GHRP).
Understanding their side effect profile is essential for
anyone considering or currently using these agents in a clinical or research setting.
---
CJC?1295 Ipamorelin: The Ultimate Guide to Growth
Hormone Peptide Therapy
CJC?1295 is a synthetic, long?acting analog of growth hormone?releasing hormone (GHRH) that
has been engineered to resist enzymatic degradation. When paired with Ipamorelin?a selective ghrelin receptor
agonist?this regimen can produce significant elevations in circulating GH and insulin?like
growth factor?1 (IGF?1). The therapeutic promise lies not only in improved body
composition but also in potential benefits
for metabolic health, tissue repair, and anti?aging.
However, as with any pharmacologic intervention that manipulates hormonal pathways, a
spectrum of side effects can arise.
Common Side Effects
Local Injection Site Reactions
The peptides are typically administered subcutaneously.
Users may experience mild erythema, induration, or occasional bruising
at the injection site. These reactions generally resolve within a few days and can be
minimized by rotating sites and using proper technique.
Fluid Retention and Edema
Growth hormone stimulates renal sodium retention and increases water reabsorption.
This can manifest as peripheral edema, particularly
in the ankles and lower legs. Some individuals report a puffiness of the
face or hands during the first weeks of therapy.
Joint Pain and Arthralgia
Elevated GH levels are associated with increased collagen turnover.
Patients often notice stiffness or discomfort in larger joints such as knees and hips, especially
after prolonged use.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Symptoms
A subset of users reports numbness, tingling, or weakness
in the hands. These symptoms correlate with fluid
accumulation around the median nerve and can be transient or persistent depending on dosage and duration.
Less Common but Notable Side Effects
Hyperglycemia or Impaired Glucose Tolerance
GH has counter?insulin effects that may raise blood glucose levels.
Regular monitoring of fasting glucose or HbA1c is advisable, particularly for those with pre?existing
metabolic conditions.
Headaches and Migraine Triggers
Some individuals experience tension?type headaches during the initial adjustment period.
These typically subside as the body acclimates to altered
hormone dynamics.
Sleep Disturbances
While GH can improve sleep architecture, paradoxically some
users report insomnia or fragmented sleep patterns when starting therapy.
Timing of injections (often in the evening) may help mitigate
this effect.
Mood Changes
Fluctuations in hormonal milieu can influence neurotransmitter pathways.
Reports include mild mood swings, irritability, or heightened anxiety,
though data are anecdotal and variable across
individuals.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
Acromegaly?like Symptoms
Sustained GH elevation over a prolonged period may lead to soft tissue swelling, joint deformities, or bone growth abnormalities.
This is extremely rare when therapy is properly monitored and dosed within recommended limits.
Cardiovascular Strain
High IGF?1 levels have been linked in some studies to
increased arterial stiffness and hypertension. Routine blood pressure checks are prudent during long?term use.
Immunogenicity
Although CJC?1295 is designed for minimal immunogenic response, occasional antibody formation has been reported.
This can reduce efficacy or lead to hypersensitivity reactions in rare cases.
Introduction to Peptide Therapy
Peptide therapy involves the administration of short chains
of amino acids that mimic natural signaling molecules in the body.
In the context of growth hormone therapy, peptides such as CJC?1295 and Ipamorelin act on specific receptors to trigger endogenous GH release rather than delivering
exogenous hormone directly. This approach offers several theoretical advantages:
Reduced Risk of Hormone Resistance
Because the pituitary gland remains active,
the feedback mechanisms that can lead to receptor downregulation are preserved.
Targeted Delivery and Lower Doses
The peptides have high affinity for GH?releasing receptors, allowing for lower systemic exposure compared to synthetic GH injections.
Improved Pharmacokinetics
CJC?1295’s resistance to proteolysis extends its half?life,
enabling once?daily or even weekly dosing schedules in some protocols.
Ipamorelin’s rapid onset complements this by providing a sharp peak of GH secretion.
Common Adverse Effects Across Peptide Therapies
Injection site discomfort
Transient swelling or edema
Mild headaches or dizziness
Hormonal imbalances (e.g., increased cortisol,
altered thyroid function)
Potential for hypoglycemia when combined with other metabolic modulators
Enhanced Body Composition
The primary clinical goal of using CJC?1295 and Ipamorelin together is to improve body composition by
increasing lean muscle mass while reducing adipose tissue.
The mechanism hinges on GH’s anabolic effects on protein synthesis, lipolysis,
and modulation of insulin sensitivity.
Positive Outcomes
Increased Muscle Hypertrophy
Enhanced IGF?1 levels promote satellite cell proliferation and differentiation,
leading to measurable gains in muscle cross?sectional area when paired with resistance training.
Fat Loss and Metabolic Efficiency
GH stimulates lipase activity, accelerating the breakdown of triglycerides.
Users often report a reduction in visceral fat deposits, improved waist circumference,
and better lipid profiles.
Improved Recovery and Endurance
Elevated IGF?1 supports connective tissue repair, potentially shortening recovery time after intense workouts and improving overall exercise performance.
Potential Body Composition Side Effects
Transient Water Retention
While beneficial for early strength gains, excess fluid can mask
true lean mass increases and temporarily inflate body weight measurements.
Altered Bone Density
GH influences bone remodeling. Short?term use is generally safe,
but long?term high doses might affect bone turnover rates, necessitating periodic densitometry in susceptible populations.
Hormonal Imbalance Impacting Body Fat Distribution
In some cases, altered sex hormone ratios (e.g., increased estrogen from aromatization of
testosterone) may influence fat deposition patterns. Monitoring
and adjusting diet or supplemental therapy can mitigate this.
Practical Considerations for Minimizing Side Effects
Start with Low Doses
Initiate therapy at the lowest effective dose, gradually titrating upward while monitoring
clinical response and adverse events.
Maintain Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
Adequate fluid intake helps manage edema and supports renal function.
Regular Monitoring
Schedule periodic blood panels to track glucose,
lipid profile, thyroid hormones, IGF?1, and cortisol levels.
Blood pressure checks should also be routine.
Optimize Injection Technique
Use a clean, sterile needle; rotate sites weekly; and consider applying gentle pressure post?injection to reduce bruising.
Complement with Lifestyle Measures
Pair therapy with balanced nutrition, sufficient sleep, and
structured resistance training to amplify benefits while mitigating risks.
In summary, CJC?1295 and Ipamorelin represent a powerful combination for growth hormone secretagogue therapy,
offering notable advantages in body composition enhancement and metabolic health.
Nonetheless, users must remain vigilant regarding side effects ranging from mild injection site reactions to more serious hormonal imbalances.
Through careful dosing, routine monitoring, and supportive lifestyle practices, many of these adverse events can be minimized, allowing individuals to reap the
benefits while maintaining safety and well?being.
that have gained popularity in the field of growth hormone therapy due to their ability to stimulate natural production of human growth
hormone (GH) while offering distinct pharmacokinetic profiles.
The combination is often referred to as a "growth hormone secretagogue" duo,
with CJC?1295 acting primarily as a sustained release analogue and Ipamorelin serving as a potent, selective GH?releasing peptide (GHRP).
Understanding their side effect profile is essential for
anyone considering or currently using these agents in a clinical or research setting.
---
CJC?1295 Ipamorelin: The Ultimate Guide to Growth
Hormone Peptide Therapy
CJC?1295 is a synthetic, long?acting analog of growth hormone?releasing hormone (GHRH) that
has been engineered to resist enzymatic degradation. When paired with Ipamorelin?a selective ghrelin receptor
agonist?this regimen can produce significant elevations in circulating GH and insulin?like
growth factor?1 (IGF?1). The therapeutic promise lies not only in improved body
composition but also in potential benefits
for metabolic health, tissue repair, and anti?aging.
However, as with any pharmacologic intervention that manipulates hormonal pathways, a
spectrum of side effects can arise.
Common Side Effects
Local Injection Site Reactions
The peptides are typically administered subcutaneously.
Users may experience mild erythema, induration, or occasional bruising
at the injection site. These reactions generally resolve within a few days and can be
minimized by rotating sites and using proper technique.
Fluid Retention and Edema
Growth hormone stimulates renal sodium retention and increases water reabsorption.
This can manifest as peripheral edema, particularly
in the ankles and lower legs. Some individuals report a puffiness of the
face or hands during the first weeks of therapy.
Joint Pain and Arthralgia
Elevated GH levels are associated with increased collagen turnover.
Patients often notice stiffness or discomfort in larger joints such as knees and hips, especially
after prolonged use.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Symptoms
A subset of users reports numbness, tingling, or weakness
in the hands. These symptoms correlate with fluid
accumulation around the median nerve and can be transient or persistent depending on dosage and duration.
Less Common but Notable Side Effects
Hyperglycemia or Impaired Glucose Tolerance
GH has counter?insulin effects that may raise blood glucose levels.
Regular monitoring of fasting glucose or HbA1c is advisable, particularly for those with pre?existing
metabolic conditions.
Headaches and Migraine Triggers
Some individuals experience tension?type headaches during the initial adjustment period.
These typically subside as the body acclimates to altered
hormone dynamics.
Sleep Disturbances
While GH can improve sleep architecture, paradoxically some
users report insomnia or fragmented sleep patterns when starting therapy.
Timing of injections (often in the evening) may help mitigate
this effect.
Mood Changes
Fluctuations in hormonal milieu can influence neurotransmitter pathways.
Reports include mild mood swings, irritability, or heightened anxiety,
though data are anecdotal and variable across
individuals.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
Acromegaly?like Symptoms
Sustained GH elevation over a prolonged period may lead to soft tissue swelling, joint deformities, or bone growth abnormalities.
This is extremely rare when therapy is properly monitored and dosed within recommended limits.
Cardiovascular Strain
High IGF?1 levels have been linked in some studies to
increased arterial stiffness and hypertension. Routine blood pressure checks are prudent during long?term use.
Immunogenicity
Although CJC?1295 is designed for minimal immunogenic response, occasional antibody formation has been reported.
This can reduce efficacy or lead to hypersensitivity reactions in rare cases.
Introduction to Peptide Therapy
Peptide therapy involves the administration of short chains
of amino acids that mimic natural signaling molecules in the body.
In the context of growth hormone therapy, peptides such as CJC?1295 and Ipamorelin act on specific receptors to trigger endogenous GH release rather than delivering
exogenous hormone directly. This approach offers several theoretical advantages:
Reduced Risk of Hormone Resistance
Because the pituitary gland remains active,
the feedback mechanisms that can lead to receptor downregulation are preserved.
Targeted Delivery and Lower Doses
The peptides have high affinity for GH?releasing receptors, allowing for lower systemic exposure compared to synthetic GH injections.
Improved Pharmacokinetics
CJC?1295’s resistance to proteolysis extends its half?life,
enabling once?daily or even weekly dosing schedules in some protocols.
Ipamorelin’s rapid onset complements this by providing a sharp peak of GH secretion.
Common Adverse Effects Across Peptide Therapies
Injection site discomfort
Transient swelling or edema
Mild headaches or dizziness
Hormonal imbalances (e.g., increased cortisol,
altered thyroid function)
Potential for hypoglycemia when combined with other metabolic modulators
Enhanced Body Composition
The primary clinical goal of using CJC?1295 and Ipamorelin together is to improve body composition by
increasing lean muscle mass while reducing adipose tissue.
The mechanism hinges on GH’s anabolic effects on protein synthesis, lipolysis,
and modulation of insulin sensitivity.
Positive Outcomes
Increased Muscle Hypertrophy
Enhanced IGF?1 levels promote satellite cell proliferation and differentiation,
leading to measurable gains in muscle cross?sectional area when paired with resistance training.
Fat Loss and Metabolic Efficiency
GH stimulates lipase activity, accelerating the breakdown of triglycerides.
Users often report a reduction in visceral fat deposits, improved waist circumference,
and better lipid profiles.
Improved Recovery and Endurance
Elevated IGF?1 supports connective tissue repair, potentially shortening recovery time after intense workouts and improving overall exercise performance.
Potential Body Composition Side Effects
Transient Water Retention
While beneficial for early strength gains, excess fluid can mask
true lean mass increases and temporarily inflate body weight measurements.
Altered Bone Density
GH influences bone remodeling. Short?term use is generally safe,
but long?term high doses might affect bone turnover rates, necessitating periodic densitometry in susceptible populations.
Hormonal Imbalance Impacting Body Fat Distribution
In some cases, altered sex hormone ratios (e.g., increased estrogen from aromatization of
testosterone) may influence fat deposition patterns. Monitoring
and adjusting diet or supplemental therapy can mitigate this.
Practical Considerations for Minimizing Side Effects
Start with Low Doses
Initiate therapy at the lowest effective dose, gradually titrating upward while monitoring
clinical response and adverse events.
Maintain Hydration and Electrolyte Balance
Adequate fluid intake helps manage edema and supports renal function.
Regular Monitoring
Schedule periodic blood panels to track glucose,
lipid profile, thyroid hormones, IGF?1, and cortisol levels.
Blood pressure checks should also be routine.
Optimize Injection Technique
Use a clean, sterile needle; rotate sites weekly; and consider applying gentle pressure post?injection to reduce bruising.
Complement with Lifestyle Measures
Pair therapy with balanced nutrition, sufficient sleep, and
structured resistance training to amplify benefits while mitigating risks.
In summary, CJC?1295 and Ipamorelin represent a powerful combination for growth hormone secretagogue therapy,
offering notable advantages in body composition enhancement and metabolic health.
Nonetheless, users must remain vigilant regarding side effects ranging from mild injection site reactions to more serious hormonal imbalances.
Through careful dosing, routine monitoring, and supportive lifestyle practices, many of these adverse events can be minimized, allowing individuals to reap the
benefits while maintaining safety and well?being.
[2025-10-05 20:20:37.583679]
URL